coupe or
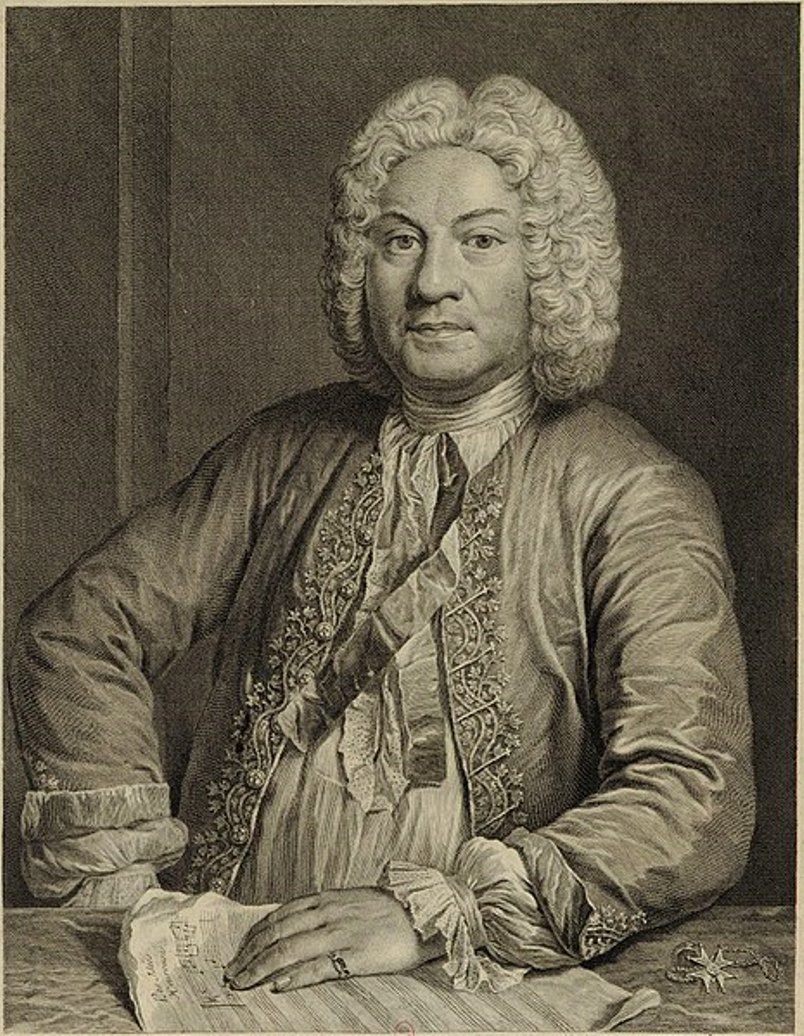

François Couperin was a French composer, organist and harpsichordist.
François Couperin is a member of a large dynasty of French musicians. At the age of 18, François succeeded his father, Charles Couperin (1638-1679), as organist at the Church of Saint-Gervais in Paris, and in 1693 he became one of the four organists of the Chapel Royal. He soon became a harpsichord teacher for the royal children, and in 1717 was appointed court harpsichordist.
François Couperin is known primarily for his harpsichord music; between 1713 and 1730 he published four books of more than 250 pieces for harpsichord. Some of them are characterized by complex accompaniment and dialogues between violin and bass, while others are light, graceful and expressive. Couperin's harpsichord pieces, even during the author's lifetime, gained great fame not only in France but also abroad. Couperin also wrote chamber music, including trio sonatas (for harpsichord and two violins) and "Royal Concertos", which he composed for Sunday evening royal entertainment. He also composed motets and other church music. Couperin's last and most significant liturgical work, Leçons de ténèbres (c. 1715), has no parallel in either French or Italian music of the period. Johann Sebastian Bach knew and appreciated this work by Couperin.
Couperin authored The Art of Touching the Clavier (1716), in which he explained in detail the technique of playing the harpsichord. And in his publications of the early 1720s, he suggested a wide variety of ways of combining French and Italian styles.
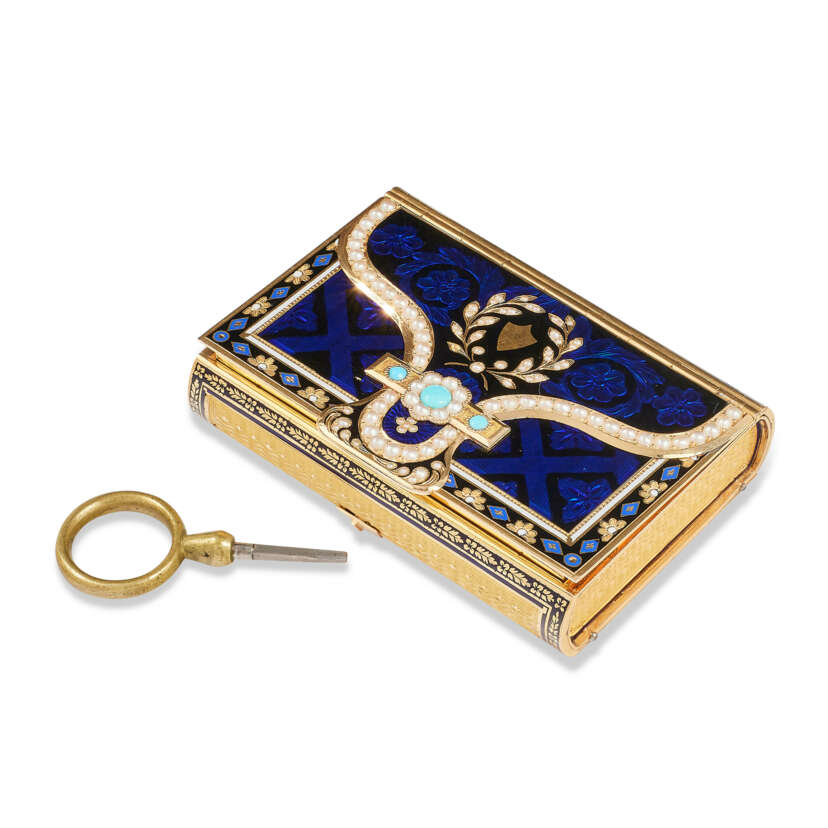







Adrien Vachette was a French jeweler of the 18th and 19th centuries, best known as the creator of the so-called Wonderful Medallion.
Vachette was one of the most famous and prolific craftsmen of his generation. He was appointed court jeweler and supplier to the court of King Louis XVIII. Gold, tortoise shell, enamel, precious stones and ornamental stones were used extensively in the creations of Vachette, particularly in the many precious snuffboxes that were in fashion at the time.
However, he became famous at a very advanced age, when he was almost 80 years old. Paris at the time was experiencing a cholera epidemic and a period of political instability. The Archbishop of Paris, Iasent-Louis de Quelan, had the idea of solving these problems by a miracle. At his behest, Vachette designed a "miraculous medallion" depicting Our Lady. Between 1832 and 1836, more than two million copies were distributed. At the same time, Archbishop Kaelan and his clergy were active in the fight against cholera. All in all, this contributed to the growth of religiosity and respect for the church in France, and the marvelous medallions of Vachette's design continue to be minted and distributed in many Western countries to this day.